The Importance of Understanding Language Skills Levels
Language skills levels play a crucial role in how we communicate and interact with others. Whether it’s speaking, listening, reading, or writing, having a good grasp of language proficiency can significantly impact our personal and professional lives.
Understanding language skills levels is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it helps us assess our own abilities accurately. By knowing where we stand in terms of language proficiency, we can set realistic goals for improvement and track our progress effectively.
Moreover, being aware of language skills levels enables us to tailor our communication to suit different contexts and audiences. For example, knowing the appropriate level of vocabulary and grammar to use when speaking to a child versus addressing a colleague in a professional setting can make a significant difference in how we are perceived.
Language skills levels also play a vital role in education and employment. Many academic institutions and employers require proof of language proficiency to ensure that individuals have the necessary skills to succeed in their respective fields. By understanding language skills levels, individuals can better prepare for exams or job interviews that assess their linguistic abilities.
Furthermore, recognising language skills levels can help promote inclusivity and diversity. By acknowledging the varying degrees of proficiency among speakers of different languages, we can create more accessible environments that cater to individuals with diverse linguistic backgrounds.
In conclusion, understanding language skills levels is key to effective communication, personal development, and social integration. By recognising the importance of linguistic proficiency and working towards improving our language skills, we can enhance our interactions with others and broaden our opportunities for success.
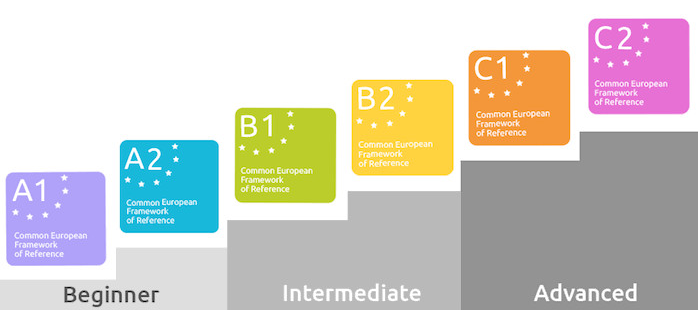
Understanding the Six Language Proficiency Levels: A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, C2
- What is A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, C2 German?
- What are language levels A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, C2?
- What are the 5 levels of spoken language?
- What is language level A1 A2 B1 B2 C1 C2?
- What are the 6 language proficiency levels?
- What are the language levels in the UK?
What is A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, C2 German?
Understanding the levels of language proficiency, such as A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, and C2 in German language skills, is essential for individuals looking to assess and improve their linguistic abilities. These levels are part of the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR) and serve as a standardised way to measure one’s competence in a foreign language. A1 and A2 represent basic language skills, while B1 and B2 indicate intermediate proficiency levels. Moving up the scale, C1 signifies advanced proficiency, with C2 representing near-native or mastery level. By familiarising oneself with these levels, language learners can better gauge their current skill set and set achievable goals for further development in the German language.
What are language levels A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, C2?
Language levels A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, and C2 are commonly used to categorise an individual’s proficiency in a particular language. These levels are based on the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR) and provide a standardised way to assess language skills across different contexts. A1 and A2 represent basic user levels where individuals can handle simple everyday communication tasks. B1 and B2 indicate independent user levels with the ability to engage in more complex conversations and written communication. C1 and C2 signify proficient user levels where individuals have advanced language skills and can express themselves fluently in various situations. Understanding these language levels helps individuals gauge their own abilities accurately and set achievable goals for language learning and improvement.
What are the 5 levels of spoken language?
The five levels of spoken language proficiency are commonly referred to as Novice, Intermediate, Advanced, Superior, and Distinguished. These levels serve as a framework for assessing an individual’s ability to communicate effectively in a particular language. Novice speakers typically have basic vocabulary and can handle simple conversations, while Intermediate speakers can engage in more complex discussions and express opinions with greater fluency. Advanced speakers demonstrate a high level of proficiency and can participate in debates and presentations on various topics. Superior speakers exhibit near-native fluency and are able to communicate effectively in professional settings. Distinguished speakers have mastered the language to the highest level, demonstrating exceptional command and understanding of nuances in communication. Understanding these levels can help individuals gauge their own proficiency and set achievable goals for language improvement.
What is language level A1 A2 B1 B2 C1 C2?
Language levels such as A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, and C2 are commonly used to categorise an individual’s proficiency in a specific language. These levels are based on the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR) and provide a standardised way to assess language skills across different contexts. A1 and A2 represent basic or beginner levels, while B1 and B2 indicate intermediate proficiency. Moving up the scale, C1 signifies advanced proficiency, and C2 represents near-native or proficient fluency. Understanding these language levels can help individuals gauge their abilities accurately, set achievable goals for improvement, and communicate their proficiency effectively in academic, professional, or social settings.
What are the 6 language proficiency levels?
The 6 language proficiency levels, commonly referred to as the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR), provide a structured framework for assessing an individual’s language skills. These levels range from A1 (beginner) to C2 (proficient), with each level indicating a different degree of linguistic ability. Understanding these proficiency levels can help individuals gauge their own language skills accurately and set achievable goals for improvement. By familiarising themselves with the characteristics and expectations associated with each level, language learners can tailor their learning strategies to progress steadily towards higher proficiency levels.
What are the language levels in the UK?
In the UK, language levels are commonly categorised according to the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR). The CEFR divides language proficiency into six levels: A1 (Beginner), A2 (Elementary), B1 (Intermediate), B2 (Upper-Intermediate), C1 (Advanced), and C2 (Proficient). These levels provide a structured framework for assessing an individual’s language skills across four key areas: speaking, listening, reading, and writing. Understanding the language levels in the UK based on the CEFR can help individuals gauge their proficiency accurately and set realistic goals for language learning and development.